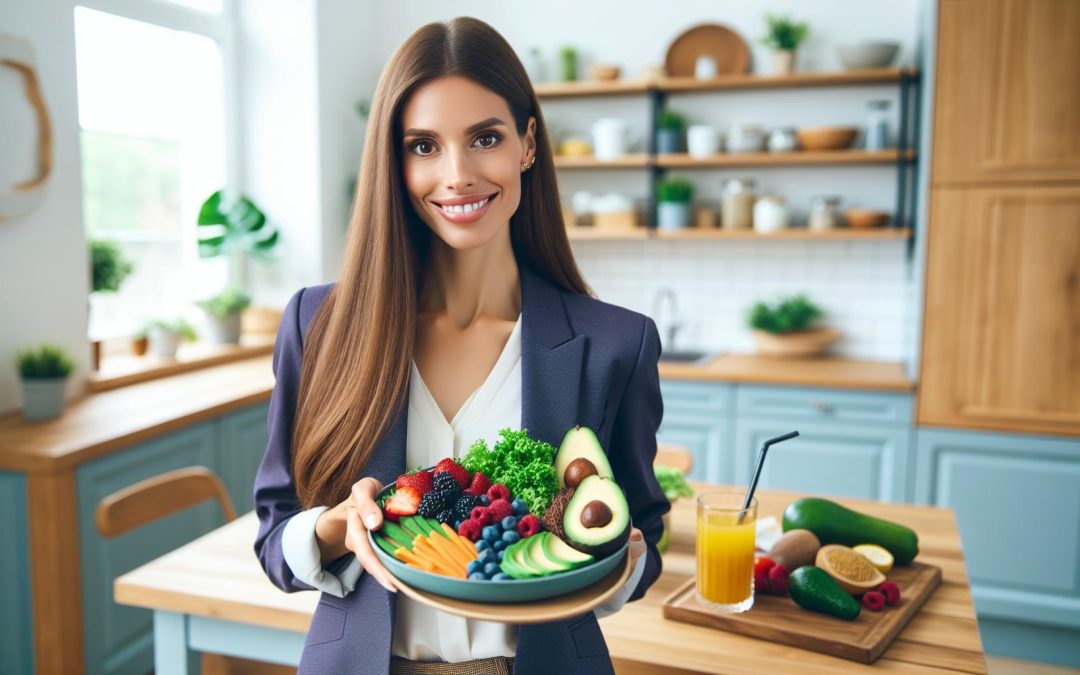
The modified keto diet is gaining traction as a more flexible approach to the traditional ketogenic lifestyle. By allowing slightly higher carb intake, it offers a sustainable option for those looking to enjoy the benefits of ketosis without the strict limitations. As this diet evolves, one crucial aspect often overlooked is maintaining proper electrolyte balance, a factor that can make or break the experience for many.
Understanding The Modified Keto Diet
The modified keto diet offers a more flexible dietary structure compared to the traditional ketogenic diet. It focuses on sustainability while maintaining the core principle of promoting ketosis.
What Makes It Different From The Standard Keto Diet?
The modified keto diet allows for a slightly higher carbohydrate intake, ranging between 50-100 grams daily, unlike the standard keto diet, which typically restricts carbs to below 20-50 grams. This adjustment reduces the strictness of meal planning and opens the door to more diverse food options, including fruits like berries and starchy vegetables such as sweet potatoes.
Protein intake is usually higher on the modified version, ensuring muscle maintenance and reducing the risk of lean muscle loss. Individuals following this approach can enjoy a protein range of 20-30% of daily caloric intake, compared to the standard keto diet’s moderate protein limits.
Additionally, this diet focuses less on fat consumption, promoting a well-balanced meal plan that fits various lifestyles. This slight relaxation makes it easier for those new to low-carb diets or those seeking to sustain their dietary changes long-term.
Its Popularity In 2025
In 2025, the modified keto diet continues gaining traction due to its adaptable nature. Many health-conscious individuals seek sustainable eating strategies that don’t sacrifice social dining or personal preferences.
Lifestyle trends lean toward flexible diets, and the modified keto’s balanced approach aligns with these preferences. It’s particularly popular among individuals looking for weight management solutions without extreme restrictions.
Healthcare professionals and dietitians increasingly recommend the modified keto diet for specific health goals, such as managing type 2 diabetes or improving metabolic health. This endorsement adds credibility, driving interest among those seeking medically-supported diets.
Social media platforms amplify its popularity, with influencers sharing recipes, meal plans, and success stories tailored to this flexible approach. Awareness and accessibility contribute to its widespread appeal in 2025.
The Importance Of Electrolyte Balance In Diets
Electrolytes regulate vital bodily functions like hydration, nerve signaling, and muscle contractions. Maintaining balanced electrolytes becomes crucial during dietary changes, such as the modified keto diet, due to their impact on overall health and wellness.
Key Electrolytes And Their Roles
Electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, magnesium, calcium, and chloride play specific roles in the body:
- Sodium supports fluid balance, blood pressure regulation, and muscle function. For example, processed foods often contain sodium, but low-carb diets rely on natural sources like salt.
- Potassium helps regulate heart function and muscle contractions. Found in foods like avocados and leafy greens, it’s vital during carb restriction.
- Magnesium aids in energy production and reducing muscle cramps. Nuts, seeds, and leafy greens are excellent sources.
- Calcium is essential for bone health and muscle movement. Non-dairy sources include kale and broccoli.
- Chloride partners with sodium to maintain fluid balance and digestion. Salt is a primary source.
A modified keto diet alters usual electrolyte intake due to changes in food choices, increasing the need to monitor and address deficiencies.
Common Electrolyte Issues On Keto Diets
Electrolyte imbalances manifest frequently in keto diets due to reduced carbohydrate intake, which depletes glycogen stores and water retention:
- Dehydration occurs when reduced insulin levels lead to quicker water and sodium loss, especially during the initial “keto flu” period.
- Muscle cramps often arise from magnesium and potassium deficiencies linked to restricted food options.
- Fatigue and weakness trace back to sodium or potassium imbalances, impacting energy levels and nerve function.
- Dizziness and headaches result from low sodium, a common issue when carb intake drops.
Addressing these issues typically involves incorporating electrolyte-rich foods, supplements, or drinks. On modified keto diets, maintaining a balanced electrolyte intake mitigates these common symptoms and supports overall well-being.
Modified Keto Diet And Electrolyte Balance 2025
The modified keto diet addresses electrolyte imbalances by integrating dietary adjustments and supplementation strategies tailored to support health and well-being. As 2025 progresses, advancements in understanding electrolyte management continue to evolve alongside this diet’s flexible framework.
How The Modified Keto Diet Addresses Electrolyte Needs
The modified keto diet emphasizes maintaining electrolyte balance by compensating for reductions in carbohydrate intake, which can deplete stored electrolytes. Sodium, potassium, magnesium, and calcium are prioritized due to their significant impact on hydration, muscle function, and nerve signaling.
Sodium intake often increases through the inclusion of broth, salted nuts, and pickled vegetables. Potassium needs are met by consuming keto-friendly options like avocados, spinach, and mushrooms. Magnesium levels remain stable through foods such as almonds, pumpkin seeds, and dark leafy greens. Calcium is sourced from dairy products and fortified plant-based milk alternatives. Electrolyte supplements are recommended for individuals experiencing persistent symptoms like fatigue or muscle cramps, especially during the initial stages of the diet.
By incorporating foods and supplements that restore lost electrolytes, the modified keto diet reduces common issues like dehydration and dizziness while supporting long-term adherence and overall success.
Current Research And Developments In 2025
In 2025, researchers focus on optimizing electrolyte management within the modified keto diet to enhance its safety and effectiveness. Studies highlight how individualized supplementation protocols, based on biomarker analyses, can address unique electrolyte needs for diverse populations.
Investigations on the relationship between electrolyte balance and chronic health conditions—such as type 2 diabetes and hypertension—examine how targeted adjustments in sodium and potassium impact health outcomes positively. Additionally, ongoing research explores the effects of combining electrolyte-rich foods, like fermented options, with the diet’s higher protein components to promote gut health and nutrient absorption.
Technological advancements bring wearable devices that monitor electrolyte markers in real time, allowing users to track hydration and electrolyte levels while adjusting their consumption accordingly. This innovation aligns with the modified keto diet’s personalized nature and sustains its appeal among health-focused individuals.
Benefits And Challenges Of The Modified Keto Diet
The modified keto diet offers a range of health benefits but also comes with challenges, especially concerning maintaining proper electrolyte balance. Understanding both aspects helps individuals make informed dietary decisions.
Health Advantages Of Proper Electrolyte Balance
Maintaining electrolyte balance supports optimal hydration, which enhances overall energy levels and reduces fatigue. Sodium and potassium play key roles in regulating fluid retention and blood pressure, ensuring cardiovascular health. Magnesium contributes to improved muscle function and prevents cramps, which are common during dietary transitions. Calcium supports bone health and aids in nerve function.
Balanced electrolytes also mitigate the risk of “keto flu,” a suite of symptoms like headaches, weakness, and dizziness caused by rapid changes in diet. Proper electrolyte levels can improve focus, ensuring cognitive efficiency during ketosis. Foods such as avocados, spinach, almonds, and dairy products promote these benefits. Including electrolyte-rich options enhances diet adherence and minimizes discomfort.
Potential Challenges And Side Effects
The modified keto diet’s reduced carbohydrate intake can lead to initial electrolyte imbalances. Symptoms like muscle cramps, dizziness, or fatigue may emerge due to rapid loss of stored electrolytes. Inadequate sodium intake may cause dehydration, while insufficient potassium and magnesium levels can exacerbate muscle spasms and lethargy.
Individuals may also find it challenging to incorporate sufficient electrolyte-rich foods like leafy greens, nuts, and dairy into their meals. In severe cases or during the early stages, supplementation might be necessary to restore balance. Over-reliance on supplements without monitoring intake risks excess electrolyte levels, which could lead to complications like hypernatremia or hyperkalemia. Adapting dietary habits effectively addresses these concerns.
Expert Recommendations For 2025
Healthcare professionals and nutrition experts emphasize strategic approaches for managing electrolyte balance on the modified keto diet in 2025. These recommendations aim to help individuals sustain optimal health and avoid common issues associated with electrolyte imbalances.
Tips For Maintaining Electrolyte Balance
Focus on consistent monitoring of electrolyte intake. Sodium, potassium, magnesium, and calcium should be prioritized to support hydration and prevent muscle cramps, fatigue, or dizziness.
Incorporate hydration routines into daily habits by drinking electrolyte-enhanced water or broths. Monitor hydration levels closely, especially during the diet’s initial stages when depletion risks are higher.
Adjust foods and supplements based on individual needs. Those with higher physical activity levels or pre-existing health conditions may require tailored electrolyte support, potentially guided by wearable devices or biomarker tests.
Adopt gradual dietary transitions. Abruptly reducing carbohydrates may exacerbate electrolyte imbalances; slower adjustments allow the body to adapt more effectively.
Prioritize timing for electrolyte replenishment. Consuming potassium and magnesium in the evening can aid muscle recovery, while sodium intake throughout the day maintains hydration.
Foods And Supplements To Consider
Include avocado and spinach for potassium, which supports muscle function. Almonds and dark chocolate offer magnesium, easing muscle cramps and tension.
Consume broth, salted nuts, and pickled vegetables as sodium sources, essential for hydration and nerve signaling. Dairy products and fortified plant-based milk provide calcium to maintain strong bones.
Electrolyte supplements address persistent imbalances. Powders, tablets, or ready-to-drink solutions with a balanced mix of sodium, potassium, and magnesium help during intense physical activity or transitions to ketosis.
Choose low-sugar electrolyte drinks to enhance hydration without excessive carbs. Products like keto-friendly sports drinks or electrolyte drops add flexibility for varying dietary preferences.
Integrate foods at regular intervals to sustain electrolyte levels. Pairing nutrient-dense options, such as leafy greens and dairy, ensures diverse electrolyte coverage throughout the day.
Conclusion
The modified keto diet continues to stand out as a flexible and sustainable option for those pursuing the benefits of ketosis. With its focus on balanced nutrition and electrolyte management, it offers a practical approach to long-term health and wellness. By addressing common challenges like electrolyte imbalances through thoughtful food choices and supplementation, individuals can enjoy improved energy and reduced discomfort.
As advancements in research and technology enhance personalization, the modified keto diet remains a promising choice for diverse lifestyles and health goals. Its adaptability ensures it stays relevant and accessible for anyone seeking a balanced, low-carb way of living.
Barbara has lost 100 pounds following the Modified Keto Diet. She started following the Keto Diet in July of 2019. She enjoyed the meals and the healthy lifestyle so much that she studied under the Speed Keto creator, Dr. Harlan Kilstein, and became a Certified Keto Coach in July 2021. After her husband was diagnosed as diabetic, she became a Certified Diabetic Coach in 2022. She coaches clients both in individual and group settings. Throughout her journey with the Modified Keto Diet, her A1C dropped from 6.5 to 4.9. She continues to enjoy healthy eating and helps others to do the same.