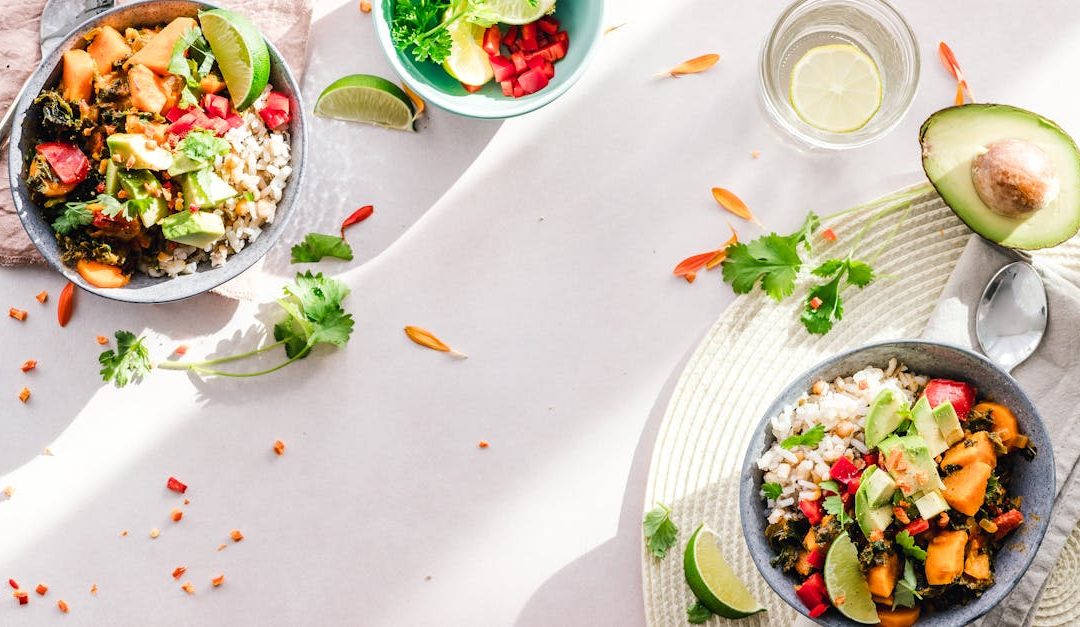
Low-carb diets like Modified Keto have gained popularity for their flexibility and focus on healthier eating habits. Unlike traditional keto, this approach allows for a bit more wiggle room with carbs, making it easier to sustain long-term. But choosing the right vegetables is key to staying on track while keeping meals delicious and satisfying.
Vegetables are a cornerstone of any healthy diet, but not all of them fit the low-carb bill. Some are surprisingly high in carbs and can quickly add up if you’re not careful. Luckily, there are plenty of nutrient-packed, low-carb options that pair perfectly with a Modified Keto lifestyle. Whether you’re meal prepping or just looking for fresh ideas, these veggies are here to keep things flavorful and guilt-free.
What Is Modified Keto?
Modified Keto is a more flexible version of the traditional ketogenic diet. It allows a slightly higher intake of carbohydrates while maintaining a focus on low-carb, high-fat eating patterns. This approach typically includes 50–100 grams of carbs per day, compared to traditional keto’s limit of 20–50 grams.
This variation caters to those looking for sustainability in their dietary habits without the stricter guidelines of standard keto. By allowing more carbs, individuals can include a broader variety of vegetables, making meals more diverse and nutrient-rich. However, the emphasis remains on keeping the body in a fat-burning state, also known as ketosis.
Protein intake in Modified Keto is moderate to high, ensuring satiety and supporting muscle health. Fat remains the primary energy source, though the balance of macronutrients is adjusted to accommodate the increased carb allotment. Healthy fats like avocados, olive oil, and nuts are staples in this diet.
People often adopt Modified Keto for its practicality and reduced risk of severe restrictions, which can be difficult to manage long-term. It can suit those pursuing weight management, improved energy levels, or better metabolic health without fully committing to the rigid structure of the standard ketogenic diet.
Benefits Of Low-Carb Vegetables In A Modified Keto Diet
Low-carb vegetables contribute essential nutrients while maintaining carb limits in a Modified Keto diet. These vegetables offer both nutritional and functional advantages to support health and wellness goals.
- Rich in Nutrients: Low-carb vegetables like spinach, zucchini, and kale provide vitamins A, C, and K, along with minerals like potassium and magnesium. These nutrients aid in immune system support, bone health, and muscle function, especially when carb sources are limited.
- High in Fiber: Non-starchy vegetables, such as broccoli and cauliflower, are excellent fiber sources. Fiber promotes gut health, improves digestion, and helps maintain satiety, making it easier to avoid high-carb snacks.
- Low Glycemic Impact: Vegetables like cucumbers and asparagus have a minimal effect on blood sugar levels, helping maintain stable energy and reducing insulin spikes common in higher-carb foods.
- Promote Ketosis: By offering nutrient density without exceeding carb allowances, these vegetables help users remain in ketosis, encouraging fat-burning and sustained energy throughout the day.
- Antioxidant Support: Vegetables such as bell peppers and Brussels sprouts are rich in antioxidants. These compounds combat oxidative stress, improving cellular health and reducing inflammation linked to chronic conditions.
- Versatile for Meal Preparation: Low-carb options such as mushrooms and green beans are highly versatile in cooking. They can be roasted, sautéed, or eaten raw, allowing variety and deliciousness in every meal.
- Aid in Weight Management: Vegetables like lettuce and cabbage are low in calories but high in water content. They help create filling, nutrient-rich meals, supporting calorie control while ensuring hydration.
- Support Metabolic Health: By replacing high-carb foods with vegetables like eggplant and zucchini, the diet may improve cholesterol levels and blood pressure. This supports overall heart health and metabolic function.
Including low-carb vegetables enhances the practicality of a Modified Keto diet, ensuring it remains nutrient-dense, flexible, and sustainable for long-term health benefits.
Factors To Consider When Choosing Low-Carb Vegetables
Selecting the right low-carb vegetables is essential for optimizing a Modified Keto diet. Factors like nutritional content, glycemic index, and flavor versatility can help in making informed choices that align with dietary goals.
Nutritional Content
Vegetables contribute essential nutrients to a Modified Keto diet while staying within carb limits. Non-starchy options like spinach and kale provide high levels of vitamins A, C, and K, essential for immunity, skin health, and bone strength. Broccoli and cauliflower are rich in fiber, promoting digestion and satiety. These options also supply micronutrients like potassium and magnesium, supporting muscle function and electrolyte balance.
Low-carb vegetables are often dense in antioxidants. For example, bell peppers deliver beta-carotene and vitamin E, while Brussels sprouts contribute potent phytonutrients. Opting for nutrient-dense options ensures that meals are balanced and packed with healthful components without exceeding daily carb intake.
Glycemic Index
Low-glycemic vegetables are crucial for maintaining stable blood sugar levels during ketosis. Options like zucchini, cucumber, and asparagus have a minimal impact on glucose, aiding energy stability throughout the day. This is particularly beneficial for those managing energy dips or blood sugar concerns on Modified Keto.
Root vegetables like carrots typically have a higher glycemic index, though they can still be included in moderation. Monitoring serving sizes of medium-carb vegetables ensures they stay within daily limits. For sustained ketosis, most vegetables chosen should rank low on the glycemic scale.
Flavor And Versatility
Vegetables with versatile profiles enhance the enjoyment of a Modified Keto diet. Broccoli and spinach adapt well to varied preparations, including stir-fries, soups, and salads. Cauliflower can replace higher-carb items like rice or mashed potatoes, adding bulk to meals without excess carbs.
Vegetables with diverse flavors, such as zucchini for noodles or cucumber for fresh snacking, make meal preparation engaging. Additionally, options like bell peppers work across cuisines, from stuffed dishes to raw snacks. Choosing flavorful, adaptable vegetables simplifies adherence to dietary goals while keeping meals satisfying.
Best Low-Carb Vegetables For Modified Keto
Modified Keto accommodates a wider range of low-carb vegetables while maintaining ketosis and supporting metabolic health. Below are categories of the best vegetables to include for nutrient-dense and flavorful meals.
Leafy Greens
Leafy greens are excellent low-carb options with high nutrient density. Spinach contains just 1.4g of net carbs per one-cup serving and provides vitamin K, magnesium, and potassium. Kale offers similar benefits, with 1.3g of net carbs per cup and antioxidants that promote overall health. Arugula, with its peppery flavor, adds variety and has 0.4g of net carbs per half cup. These greens are versatile, suitable for salads, smoothies, or sautéed dishes. Their fiber content aids digestion, supporting gut health while staying within carb limits.
Cruciferous Vegetables
Cruciferous vegetables are fiber-rich, low-carb options. Broccoli contains 4g of net carbs per cup, making it a popular choice for soups and stir-fries. Cauliflower, with 3g of net carbs per cup, works well as rice, mashed, or roasted. Brussels sprouts provide 4.7g of net carbs per cup and are ideal for baking or pan-frying with healthy fats. These vegetables are high in vitamin C and antioxidants, supporting immunity and reducing inflammation, essential for a well-rounded Modified Keto diet.
Allium Vegetables
Allium vegetables add flavor and nutrients to meals without exceeding carb restrictions. Garlic contains about 1g of net carbs per clove and offers compounds supporting heart health. Onions, with 5g of net carbs per half cup, work well caramelized or fresh in salads. Green onions, a milder alternative, provide 1.2g of net carbs per two tablespoons and can be used as toppings. Despite their slightly higher carb count, they are highly nutrient-dense and add depth to dishes.
Other Low-Carb Options
Additional vegetables bring variety without compromising carb goals. Zucchini has 2.1g of net carbs per one-cup serving and is ideal for zoodles or grilling. Bell peppers, particularly red and green, range from 3-4g of net carbs per half cup and provide vitamin A and C. Mushrooms contain just 2.3g of net carbs per cup and are great for stuffing, soups, or as side dishes. Asparagus, with 2g of net carbs per half cup, is another versatile option, perfect for roasting or steaming.
Tips For Incorporating Low-Carb Vegetables Into Meals
Plan Ahead
Allocating time to plan meals helps ensure the inclusion of diverse low-carb vegetables like spinach, zucchini, or broccoli. Preparing a weekly menu allows for balanced dishes, reducing the chances of missing essential nutrients while staying within carb limits.
Focus on Versatility
Choosing adaptable vegetables like cauliflower and bell peppers makes it easier to experiment with recipes. For example, cauliflower can be used in rice, pizza crusts, and mashed dishes, while bell peppers can be stuffed, roasted, or added to salads.
Try Simple Substitutions
Replacing high-carb staples with low-carb vegetable alternatives is effective. Zucchini noodles work well instead of pasta, lettuce wraps replace tortillas, and mashed cauliflower serves as an alternative to mashed potatoes.
Add Flavor with Herbs and Spices
Enhancing low-carb vegetables with herbs, spices, or healthy fats like olive oil improves taste without significantly raising carb counts. Basil and garlic pair well with spinach, while rosemary complements roasted asparagus.
Pre-Cut and Pre-Cook Veggies
Washing, chopping, and pre-cooking vegetables like kale or Brussels sprouts saves time and ensures they’re ready for quick meals. This approach helps maintain regular vegetable consumption, especially during busy days.
Incorporate Into All Meals
Adding low-carb vegetables into every meal promotes consistent nutrient intake. Include spinach or mushrooms in omelets for breakfast, zucchini noodles at lunch, and a side of roasted broccoli for dinner.
Use Them in Snacks
Low-carb vegetable snacks offer nutrient-rich alternatives to carb-heavy options. Sliced cucumbers, celery sticks with nut butter, or roasted kale chips provide satisfying choices between meals.
Blend into Smoothies
Blending greens like kale or spinach into smoothies boosts nutrient levels without adding many carbs. Combining them with unsweetened almond milk or avocado keeps carbohydrate counts low while enhancing flavor and texture.
Conclusion
Choosing the right low-carb vegetables can make all the difference in maintaining a sustainable and enjoyable Modified Keto lifestyle. With so many nutrient-packed options available, it’s easy to create meals that are both flavorful and aligned with dietary goals. From leafy greens to versatile veggies like zucchini and bell peppers, these choices bring variety and balance to every plate.
By incorporating practical tips like planning ahead and experimenting with recipes, anyone can make low-carb eating a seamless part of their routine. The flexibility of the Modified Keto approach allows for creativity in the kitchen while staying on track. With the right vegetables, this diet becomes more than just a way to eat—it’s a path to better health and satisfaction.
Barbara has lost 100 pounds following the Modified Keto Diet. She started following the Keto Diet in July of 2019. She enjoyed the meals and the healthy lifestyle so much that she studied under the Speed Keto creator, Dr. Harlan Kilstein, and became a Certified Keto Coach in July 2021. After her husband was diagnosed as diabetic, she became a Certified Diabetic Coach in 2022. She coaches clients both in individual and group settings. Throughout her journey with the Modified Keto Diet, her A1C dropped from 6.5 to 4.9. She continues to enjoy healthy eating and helps others to do the same.