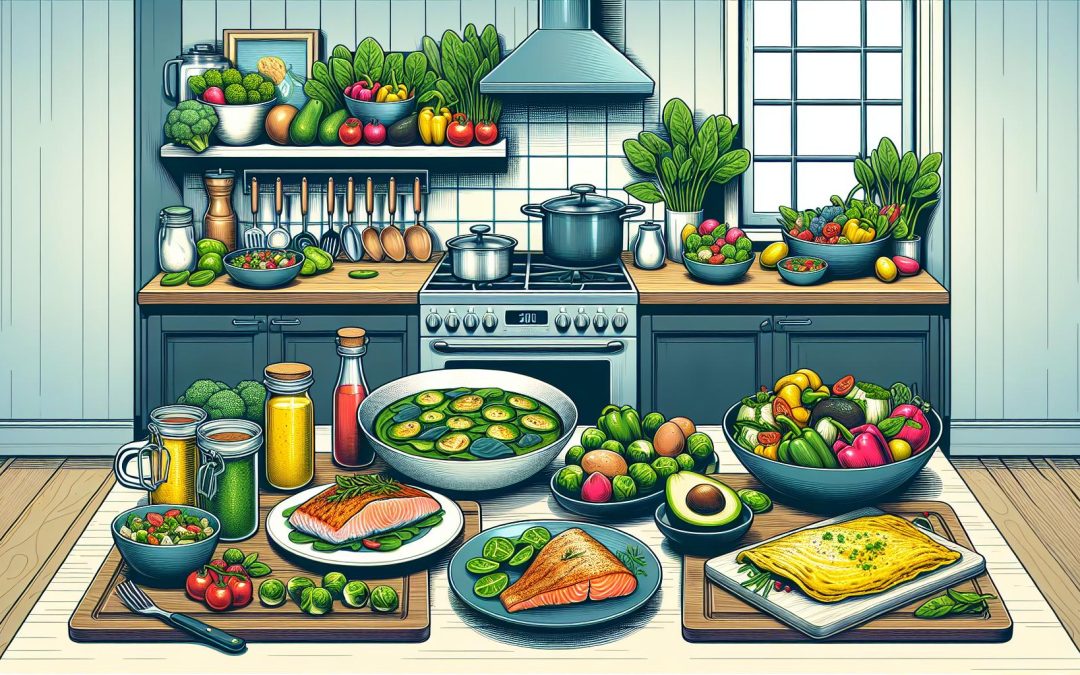
Living with diabetes often means navigating a maze of dietary restrictions, but it doesn’t have to be a dull journey. Low-carb modified keto meals offer a delicious and manageable way to keep blood sugar levels in check while still enjoying flavorful dishes. These meals are not only low in carbs but also packed with nutrients that support overall health.
Whether you’re new to the keto lifestyle or a seasoned pro looking for diabetic-friendly options, these 16 recipes will add variety to your meal plan. From savory breakfasts to satisfying dinners, each dish is designed to be both tasty and beneficial for managing diabetes. Get ready to explore a world of culinary possibilities that align with your health goals.
Understanding Low-carb Modified Keto Meals
Diabetics can enjoy low-carb modified keto meals that are not only delicious but also effective in managing blood sugar levels. These meals offer a balanced approach between strict ketogenic protocols and flexible eating habits for better glycemic control.
What Is a Modified Keto Diet?
A modified keto diet maintains a low-carb intake but allows slightly more carbohydrates than the traditional ketogenic diet. This approach makes it easier to sustain while still promoting ketosis, a state where the body uses fat as its primary energy source. Typically, carbohydrate intake is limited to 50-100 grams per day, as opposed to the strict keto limit of 20-50 grams.
The modified keto diet focuses on whole foods, including lean proteins (chicken, fish), healthy fats (avocado, olive oil), and non-starchy vegetables (spinach, broccoli). This diet also reduces the likelihood of nutrient deficiencies which can occur in stricter forms of keto by providing more room for a varied and balanced nutrient intake.
For instance, a breakfast on a modified keto diet might include an omelet with spinach and mushrooms, drizzled with olive oil. Lunch could be a grilled chicken salad with avocado and a low-carb dressing.
Benefits for Diabetics
Low-carb modified keto meals offer multiple benefits for diabetics. First, they help regulate blood sugar levels due to the limited carbohydrate intake, reducing glucose spikes after meals. Controlled studies, including those by the American Diabetes Association, have shown that low-carb diets significantly lower HbA1c levels, a marker of long-term blood glucose control.
Reduced carbohydrate intake also aids in weight management, crucial for type 2 diabetics. Better weight control improves insulin sensitivity. Additionally, the inclusion of healthy fats and proteins in every meal promotes satiety, reducing the likelihood of overeating and stabilizing energy levels throughout the day.
Moreover, a modified keto diet can enhance cardiovascular health. By focusing on healthy fats, this diet lowers bad cholesterol (LDL) and increases good cholesterol (HDL), decreasing the risk of heart disease, a common concern for diabetics.
For example, a dinner option might include baked salmon with a side of roasted Brussels sprouts, providing a nutrient-rich meal that supports overall health.
Nutritional Breakdown
Low-carb modified keto meals for diabetics not only help manage blood sugar levels but also provide balanced nutrition. This section breaks down the essential macronutrients and micronutrients in these meals.
Macronutrient Ratios
Low-carb modified keto diets balance macronutrients to sustain energy and control blood sugar. Typically, the diet comprises 50-70% fat, 20-30% protein, and 5-10% carbohydrates. This balance ensures that carbs don’t spike blood sugar levels, proteins help with muscle maintenance, and fats provide long-lasting energy.
- Fat: Avocado, olive oil, and fatty fish like salmon.
- Protein: Lean meats, eggs, and tofu.
- Carbohydrates: Non-starchy vegetables such as spinach, broccoli, and cauliflower.
For instance, a dinner plate might include baked salmon (high in fat and protein) with a side of roasted Brussels sprouts (low in carbs) drizzled in olive oil. This combination aligns with the macronutrient ratios, ensuring balanced meals while managing diabetes.
Essential Micronutrients
Micronutrients are crucial for overall health, particularly for those managing diabetes. Low-carb modified keto meals often include foods high in essential vitamins and minerals.
- Vitamin C: Found in broccoli and bell peppers, boosts the immune system.
- Vitamin K: Present in leafy greens like kale and spinach, supports blood clotting.
- Magnesium: Nuts and seeds offer magnesium, which helps regulate blood sugar.
- Potassium: Avocados and mushrooms provide potassium, crucial for heart health.
Incorporating a variety of these foods into daily meals ensures diabetics receive essential micronutrients. For example, an omelet with spinach and bell peppers supplies vitamins C and K, enhancing nutritional value without increasing carbs.
Top 16 Low-carb Modified Keto Meals for Diabetics
Including low-carb modified keto meals can help diabetics manage their blood sugar levels without sacrificing taste. The following are curated options for breakfast, lunch, dinner, and snacks.
Breakfast Options
- Spinach Omelet: Packed with protein, this omelet includes fresh spinach and feta cheese. It’s low in carbs and high in iron and fiber.
- Avocado Egg Cups: Serve half an avocado baked with an egg. Avocados are high in healthy fats and eggs add protein.
- Chia Seed Pudding: Mix chia seeds with unsweetened almond milk and let it sit overnight. Top with a few berries for added flavor and minimal carbs.
- Smoked Salmon and Cream Cheese Roll-Ups: Roll smoked salmon slices with cream cheese. Add capers and dill for added zest and nutritional value.
- Greek Yogurt with Nuts: Choose unsweetened Greek yogurt and top with a handful of almonds or walnuts for added protein and healthy fats.
Lunch Ideas
- Grilled Chicken Salad: Combine grilled chicken breast with mixed greens, cucumber, tomatoes, and olive oil dressing. It’s low-carb and high in protein.
- Cauliflower Rice Stir-fry: Stir-fried with non-starchy vegetables and a lean protein like shrimp, this meal is both filling and nutritious.
- Zucchini Noodles with Pesto: Use a spiralizer for zucchini and toss with homemade pesto. This dish is rich in flavor and low in carbs.
- Turkey and Avocado Lettuce Wraps: Replace bread with lettuce leaves and fill with turkey slices, avocado, and a dash of mustard.
- Egg Salad Lettuce Cups: Mix hard-boiled eggs with a bit of mayonnaise and place on romaine lettuce leaves.
Dinner Recipes
- Baked Salmon with Brussels Sprouts: Roast salmon alongside Brussels sprouts. It’s rich in omega-3 fatty acids and fiber.
- Chicken Alfredo with Zoodles: Substitute traditional pasta with zucchini noodles and chicken breast in a creamy Alfredo sauce.
- Stuffed Bell Peppers: Fill bell peppers with ground turkey, tomatoes, and cauliflower rice. Bake until tender.
- Beef and Broccoli Stir-fry: Combine lean beef strips with broccoli florets in a soy sauce-based marinade. This dish provides protein and fiber.
- Creamy Spinach and Mushroom Pork Chops: Sear pork chops and then cook with a creamy spinach and mushroom sauce. It’s low in carbs and rich in taste.
- Cheese and Almonds: Pair a few slices of cheese with a handful of almonds. It’s a perfect blend of protein and healthy fats.
- Cucumber Slices with Hummus: Slice cucumbers and dip them in hummus for a low-carb, nutrient-rich snack.
- Pork Rinds: A crunchy, zero-carb option that’s perfect for snacking and adds texture to meals.
- Olives and Cheese Sticks: A combination of healthy fats and protein, great for keeping energy levels stable.
- Hard-boiled Eggs: Easy to prepare and portable, providing essential protein and fats while being carb-free.
How to Incorporate These Meals into Your Diet
Incorporating low-carb modified keto meals into a diabetic diet ensures enjoyable and healthful eating without compromising blood sugar management. Following these tips helps streamline the transition and maintain consistency.
Planning Your Weekly Meals
Organizing meals ahead of time simplifies adoption of low-carb modified keto meals. Start by setting aside time once a week to plan breakfasts, lunches, dinners, and snacks. Use a meal planner to outline each day’s menu, ensuring diverse options like spinach omelets for breakfast, grilled chicken salad for lunch, and baked salmon with Brussels sprouts for dinner.
Batch cooking is another effective strategy. Cook large portions of keto-friendly foods and store them in portion-sized containers. For example, prepare a large batch of zucchini noodles with pesto for quick lunches or dinners throughout the week.
Varying proteins (e.g., chicken, fish, tofu) and incorporating different types of non-starchy vegetables (e.g., spinach, zucchini, Brussels sprouts) prevents monotony and ensures balanced nutrient intake. Remember to consider any social engagements or planned activities that may affect meal schedules and pack appropriate snacks like cheese and almonds or cucumber slices with hummus.
Shopping Tips
Creating a shopping list tailored to low-carb modified keto meals aids in efficient grocery trips. Start by listing essential items from the meal plan, focusing on whole foods such as avocados, olive oil, lean meats, and non-starchy vegetables.
Stick to the perimeter of the grocery store where fresh produce, meats, and dairy are typically located. Avoid aisles containing processed foods high in carbohydrates. For instance, choose leafy greens, fresh proteins, and healthy fats, steering clear of packaged snacks and sugary items.
Buying in bulk, especially for frequently used ingredients like nuts or seeds, can be cost-effective. Look for discounts on lean meats and opt for seasonal vegetables to save money. Purchasing versatile items like eggs and cheese allows for various meal preparations.
Consider shopping online for specialty keto products if they’re unavailable locally. Many online retailers offer a range of keto-friendly ingredients and snacks, ensuring a wider variety of low-carb options.
Precautions and Considerations
When transitioning to a low-carb modified keto diet for diabetes management, several factors should be considered to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Potential Side Effects
Adopting a low-carb modified keto diet may induce certain side effects, especially during the initial adaptation period. Some individuals experience symptoms collectively known as the “keto flu,” which can include headaches, fatigue, dizziness, and irritability. These symptoms generally subside within a week as the body adjusts to using fat for energy instead of carbohydrates.
Another potential side effect is constipation, often due to insufficient fiber intake. Consuming non-starchy vegetables like broccoli, spinach, and cauliflower helps alleviate this issue. Additionally, individuals may experience dehydration and electrolyte imbalances. Drinking plenty of water and consuming foods rich in electrolytes, such as avocados and leafy greens, can help maintain balance.
Hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, is a concern for diabetics, particularly when medications are adjusted without proper medical guidance. Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly and adjusting medications under a healthcare provider’s supervision is crucial to avoid potentially dangerous drops in blood sugar.
Consulting with Your Healthcare Provider
Before starting a low-carb modified keto diet, consulting with a healthcare provider is essential. A healthcare provider can tailor dietary recommendations to an individual’s specific health needs and conditions, ensuring safety and effectiveness. They can also help adjust any diabetes medications to prevent hypoglycemia and other complications.
Continuous monitoring by a healthcare provider is vital, especially during the early stages of the diet. Regular check-ups can help track progress, adjust the diet as necessary, and address any emerging health concerns. Blood tests to monitor kidney function, liver function, and cholesterol levels are often recommended to ensure no adverse effects arise from dietary changes.
Individuals should also discuss any pre-existing health conditions, such as cardiovascular disease or kidney disease, with their healthcare provider. Certain conditions may require adaptations to the standard low-carb modified keto diet to prevent complications. For example, those with kidney disease might need to monitor protein intake more closely.
Ensuring a comprehensive evaluation tailored to individual health profiles allows for a safe and sustainable transition to a low-carb modified keto diet while managing diabetes effectively.
Conclusion
Adopting a low-carb modified keto diet can be a game-changer for those managing diabetes. By incorporating delicious and nutritious meals, individuals can enjoy a varied diet while effectively controlling blood sugar levels. The flexibility of this approach allows for a balanced intake of carbohydrates, making it easier to maintain long-term.
With practical tips and a range of meal options, anyone can seamlessly integrate these recipes into their daily routine. Remember to consult with a healthcare provider to ensure a safe transition. Embrace the journey towards better health with these flavorful and satisfying low-carb modified keto meals.
Barbara has lost 100 pounds following the Modified Keto Diet. She started following the Keto Diet in July of 2019. She enjoyed the meals and the healthy lifestyle so much that she studied under the Speed Keto creator, Dr. Harlan Kilstein, and became a Certified Keto Coach in July 2021. After her husband was diagnosed as diabetic, she became a Certified Diabetic Coach in 2022. She coaches clients both in individual and group settings. Throughout her journey with the Modified Keto Diet, her A1C dropped from 6.5 to 4.9. She continues to enjoy healthy eating and helps others to do the same.